Generative AI Deployment: Generating Dynamic Outputs from User Inputs with Server-less Infrastructure
Creating an efficient Server-less Application using Lambda for Seamless AI Integration and Processing"
Generative AI refers to a class of artificial intelligence techniques that enable computers to generate content, such as images, text, or even music, autonomously. Unlike traditional AI systems that rely on predefined rules or patterns, generative AI models are trained on large datasets and can produce new, original content that closely mimics human creations.
Generative AI Deployment involves implementing generative AI models into real-world applications. This process typically involves integrating the AI model with existing infrastructure, such as cloud services or APIs, to process user inputs and generate relevant outputs. Deploying generative AI effectively requires considerations such as scalability, efficiency, and ethical use of the generated content.
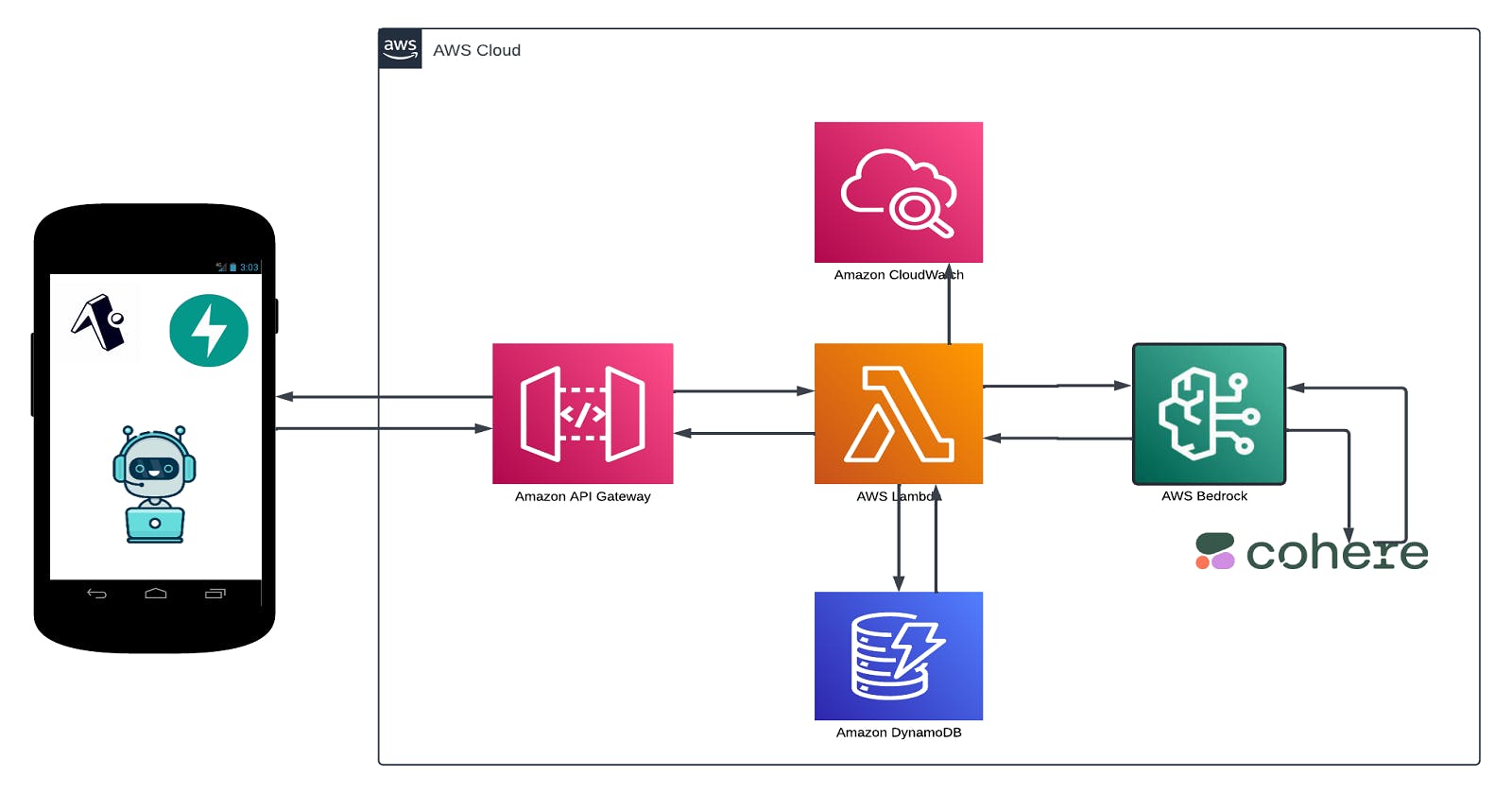
In this guide, I'll walk you through the steps to deploy a generative AI model using serverless infrastructure. We'll make use of serverless technologies such as AWS Lambda, API Gateway, and DynamoDB to efficiently handle user inputs, process them through the AI model, and deliver dynamic outputs.
Setting up Infrastructure
First, we'll get access to CohereAI through Amazon Bedrock. Next, we will head over to DynamoDB and create a table, storing everything from user inputs to the generated outputs, We'll then create Lambda function that connects seamlessly with CohereAI via Amazon Bedrock. for API Gateway. We'll use it to create an endpoint that'll expose our Lambda function as a RESTful API and also cloudwatch to store the logs of all the activities going on.
NB: Everything will be deployed in us-west-2 (Oregon), and all resources have to be in the same region for it to work seamlessly.
Step 1. Setting up access to AWS Bedrock
Head over to the aws Console and search Bedrock, should be a shiny new green icon that looks like this, select it and click "get started"
On the panel on the left select model access and then in the middle click on "manage model access", follow the prompt, select the model you want to use, in this case cohereai and click request access, it should quickly give you access to use the models, i believe most of them are generally available to the public.

You should be granted access fairly quickly and ready to use. Next up storage
Step 2. Creating the db for storage
Head on to the aws console, search for dynamodb and get started

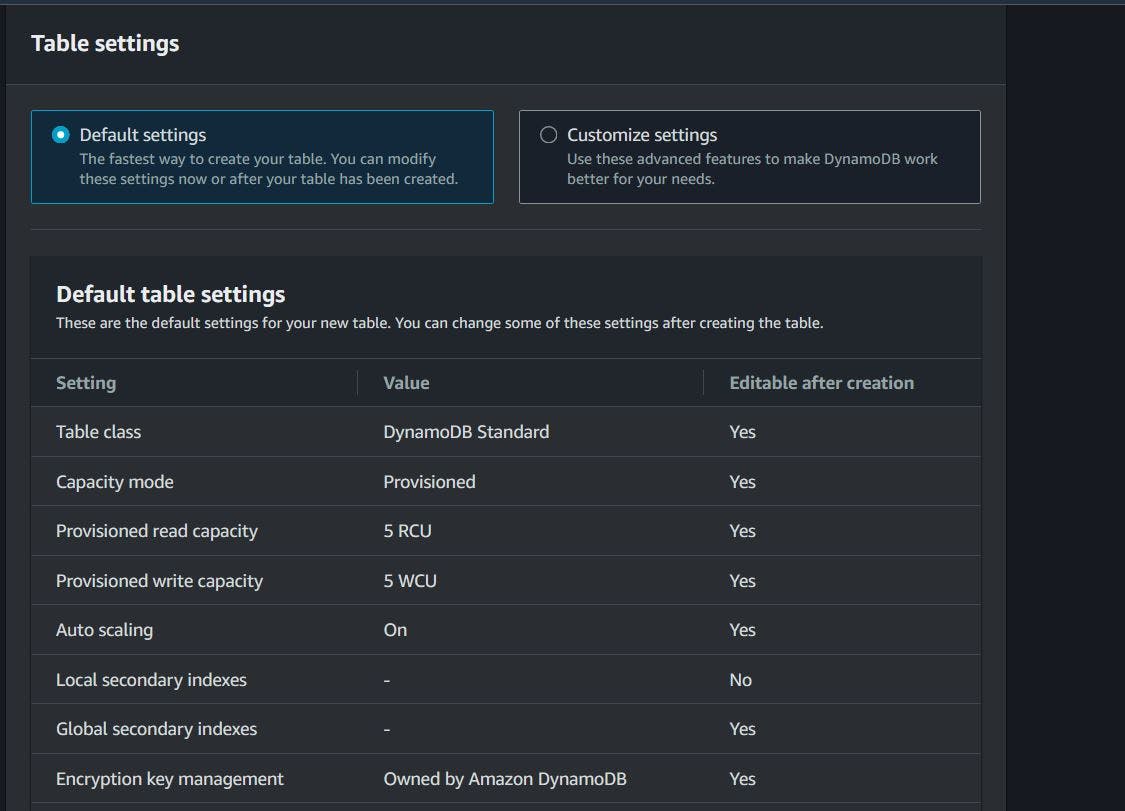
Click on create table and fill in the details

take note of the name as we will refer to it in the lambda function, Leave the remaining options as default and click create,
we should have a fresh db ready to go.

Step 3a. Create our lambda roles and permission
Before we go running to create our lambda, which is the brains of the operations. we need to give the service permissions to call some other services on our behalf. we will create the following permissions
Dynamodb full access: To be able to CRUD the db
Cloudwatch full access: To store logs and activities
Bedrock Full access: To be able to send and receive information for the bedrock service.
We can do all these at once, so head over to IAM and create a role.

remember the name of the role, so that we can apply it when we are creating the lambda function.
Step 3b. Create our lambda function
Buckle up, as we have a lot to do here. ready? head over to the console and search for lambda, usually the 1st thing to pop up.

Here we are going to author our function, give it a name and set the runtime to a python runtime, NB:Please select a runtime of v3.11, as we need the version of boto3 to be at-least > v1.28.
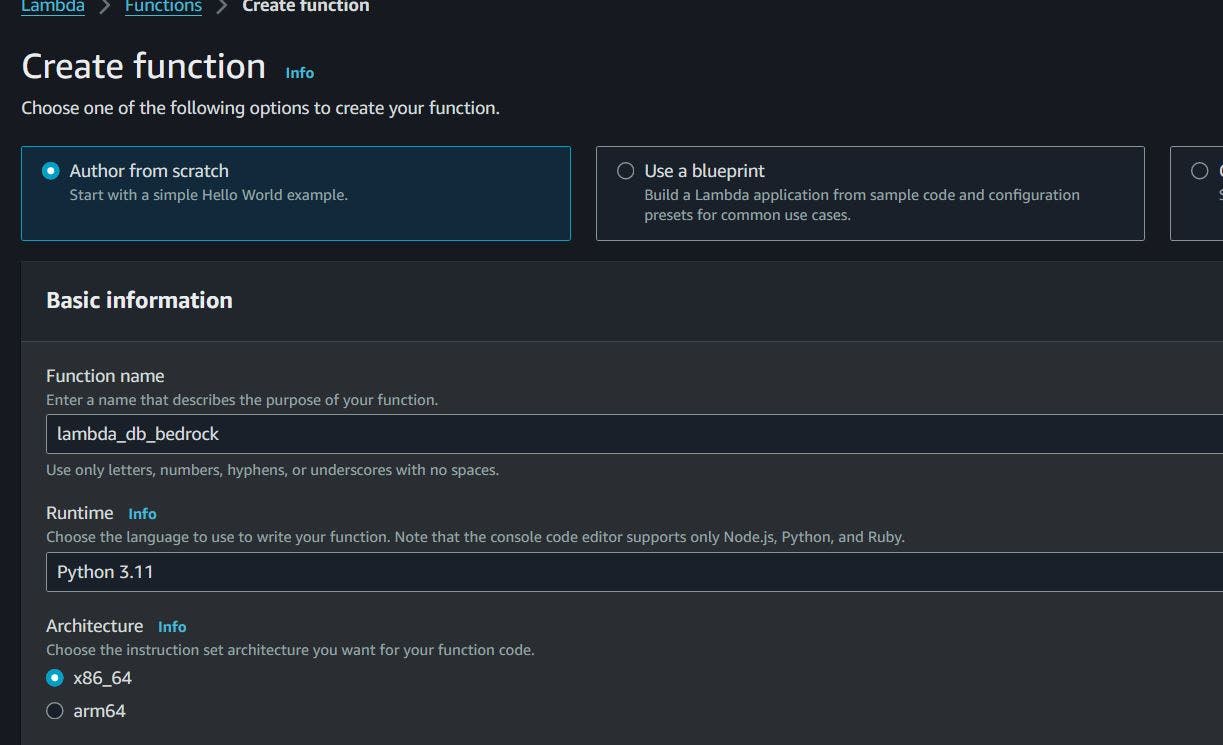
Under the permissions section, select an existing execution role, and select the role we created earlier in the IAM section and then go ahead and create the function.

go ahead and click create... and lets get to it.
briefly lets check the version of boto3 before we continue,
import boto3
print(boto3.__version__, "<- show boto3 version")

click on deploy then test, then we should see the outcome in the execution results

Great our boto3 version is okay, we can now proceed to write our actual function, the function will receive the user prompt and send it to aws bedrock which will process it using the cohereAI model and send us a dynamic response.
Now we can replace the code with our actual code.
import json
import boto3
# import resources
client = boto3.client("bedrock-runtime")
dynamodb = boto3.resource("dynamodb")
table = dynamodb.Table("<DynamoDbTableName>")
# check the version of boto3
print(boto3.__version__, "<- boto3 version")
def lambda_handler(event, context):
# the prompt will be received as an event from api-gw
print(event)
user_prompt = event["user_prompt"]
# create a response object,should be in json format
response = client.invoke_model(
accept="application/json",
contentType="application/json",
modelId="cohere.command-text-v14",
body=json.dumps(
{
"prompt": user_prompt,
"max_tokens": 20,
"temperature": 0.9,
}
),
)
print(response["body"])
# convert the response body to bytes, then back to string
response_byte = response["body"].read()
response_string = json.loads(response_byte)
# Extracting AI response from the response
ai_response = response_string["generations"][0][
"text"
]
# Store user prompt and AI response in DynamoDB table
response_db = table.put_item(
Item={"user_prompt": user_prompt, "ai_response": ai_response}
)
print(response_db)
return {
"statusCode": 200,
"body": json.dumps(
{"response_string": response_string,"response_db": response_db,}
),
}
Click on deploy then test, then we should get a response from our model.
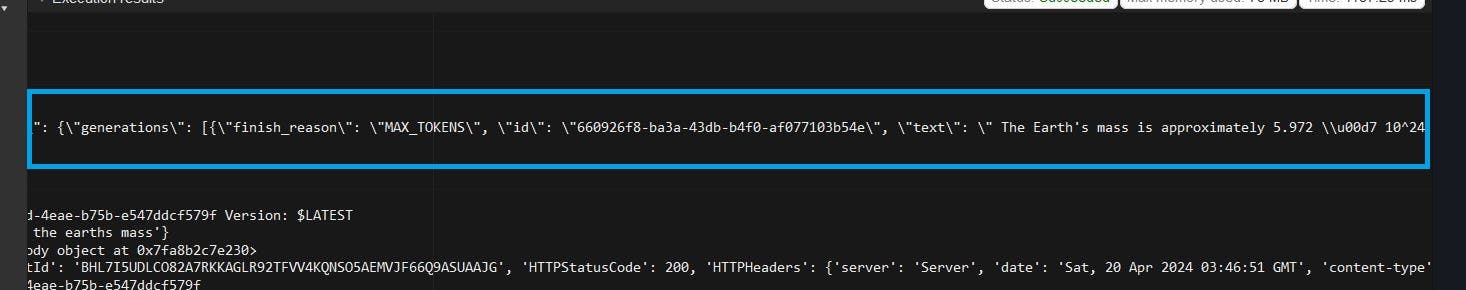
Great our lambda function is working fine,its sending and receiving prompts and also storing it in the db. We can now proceed to the final steps and create API gateway
Step 4. Create and manage API gateway
Stay with me we are almost done, head over to the aws console and search for API gateway

Click "create" then lets create another api endpoint,Select restapi and give it a name then set the api endpoint type to be regional. you should now have api

Click on create resource and give the path endpoint a resource name, lets say "/" and "chatwithcohere"

You should now have something like this

the next part is little tricky but follow along, we are going to do 3 things
create the get method and point it to the lambda
create a mapping for the query params
deploy the api and test
A. Create "GET" method
Click create method, select the method type to be "GET" and set the integration type to be lambda

B. Create a mapping for the query params
while still in the creation of the "GET", scroll down to the Method request settings, set the following
authorization : None
request validator : Validate query string parameters and headers
for the URL query string parameters set the following
name : user_prompt
required: true
Click create and then lets deploy the api

C. Deploy the API
on the resource page of the API, click the deploy api button set the stage to new stage and give it a name, then deploy it
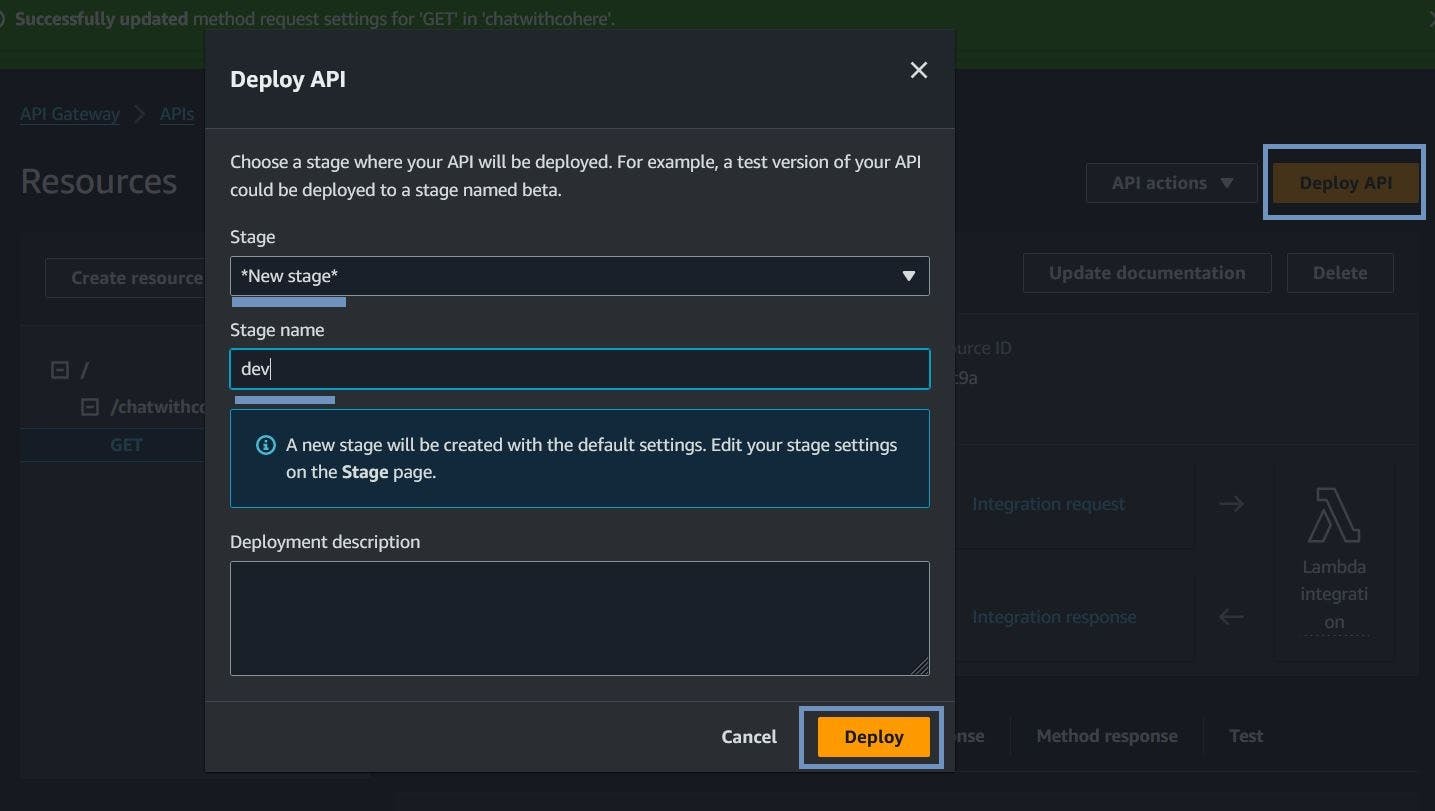
Great, our application has been deployed and we have our end point, on the panel on the left select stages, select the stage and view the invoke url

With that we can now test our end point here on the console. go to the test tab, input the user_prompt, which is the query string
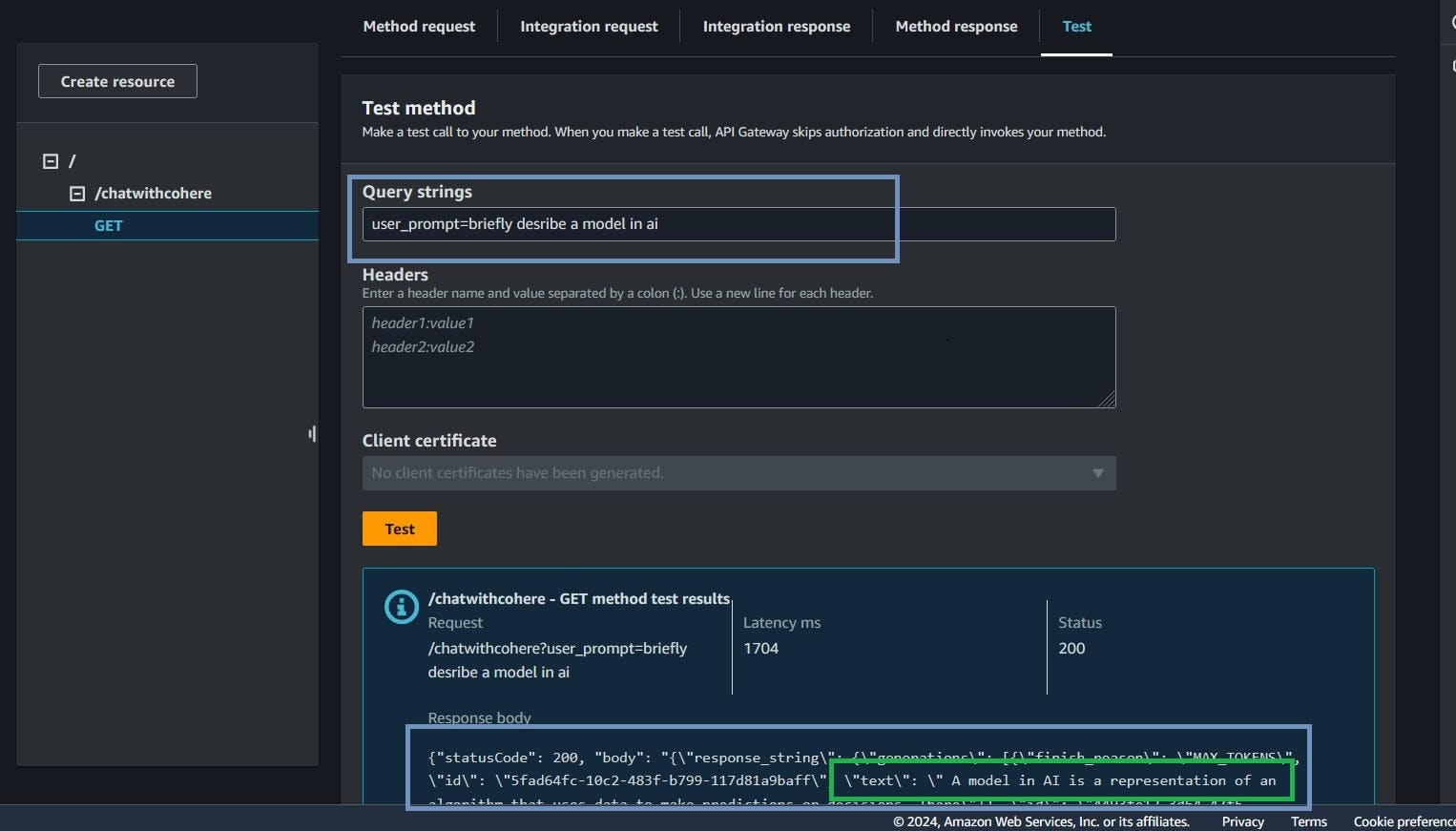
Congratulations are in order! With our serverless infrastructure now successfully deployed, we can communicate with our generative ai model with a serverless infrastructure
In conclusion, Once the API Gateway is set up and running, you can integrate it into your application seamlessly. For instance, if you're using a FastAPI server, incorporating the API Gateway endpoint is a breeze. You simply define it as one of the endpoints your FastAPI server handles.
Clean up
So far we created 3 resources api gateway,lambda and dynamodb that can be terminated go to the console page of each resource that was created, select the resource click actions > delete on the top right.
🚧🚧🚧Don't forget to delete all your resources when you are done!🚧🚧🚧